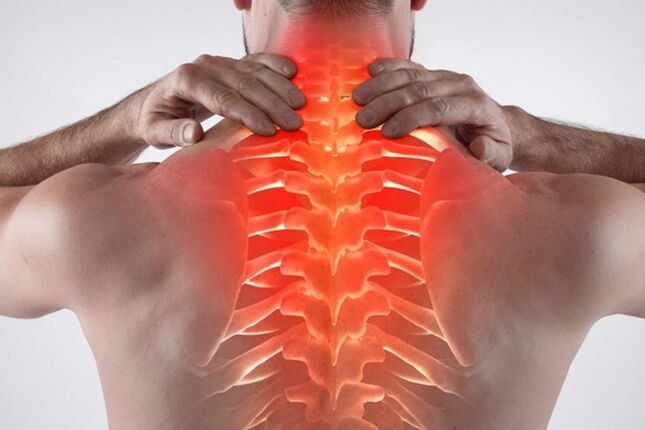
Osteochondrosis of the breast is a common degenerative disease. There are specific symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis, which indicates the onset of the pathology. In the initial stages, the discomfort does not bother the patient much, so he is in no hurry to seek help from a specialist. Over time, the symptoms worsen, forcing the patient to go to the doctor, where a neglected pathology is found. You need to know what early signs determine osteochondrosis and what treatments are most effective.
What is thoracic osteochondrosis and how it occurs
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic region is characterized by the appearance of destructive-dystrophic processes in the middle part of the ridge. The destruction is located between the 8th and 19th vertebrae. To find out which vertebra is affected, it is necessary to perform accurate diagnostic tests. Thoracic osteochondrosis is often accompanied by terrible complications, including prolapse or hernia. Without complications, the disease is rare, as the destruction of cartilage tissue inevitably leads to the destruction of the entire spinal frame.
When the patient develops a circulatory disorder or age-related wear and tear on the joints, the fibrous ring located in the cavity of the intervertebral disc begins to collapse, losing its normal structure. As the destruction is slow, then in the initial stages microcracks appear, through which the nucleus pulposus seeps.
With the leakage of the inner component, the annular fibrosis begins to weaken, leading to gradual stretching and tearing. When the pulpal nucleus protrudes, an intervertebral hernia occurs, which is the most common complication of osteochondrosis. The pathology involves damage to cartilage tissue, which causes significant discomfort. Severe back pain is also associated with neurological syndromes that develop from pinching or irritating nerve roots.
Symptoms of breast osteochondrosis
In the initial stage, the patient does not feel discomfort, therefore at this stage the disease can be detected only by accident. The disease has many symptoms that can be disguised as other pathologies.
The symptoms of osteochondrosis in the chest can be felt by the following manifestations:
- Breathing is difficult. Problems occur with shortness of breath and shortness of breath. This indicates damage to the thoracic spine and spinal cord.
- The main symptom is chest pain. There is also a pressing feeling in the heart, more reminiscent of an ischemic attack.
- Discomfort occurs when the back bends. As the disease progresses, the pain in this position increases.
- Against the background of poor blood circulation there is a feeling of cold in the lower or upper extremities.
- Chest pain on the background of emerging intervertebral hernias. The discomfort is often felt more strongly on the left or right side of the affected area.
- Throat discomfort and swallowing problems. If there is irritation of the nerve endings in the upper chest area, a cough occurs.
- Women may experience chest pain that is not related to cyclical changes or hormonal imbalances.
- There is a tingling or burning sensation in the legs and feet.
- Hair and nails become brittle, dull.
- Shingles is less common.
- Back and chest pain occur at the same time.
- Less commonly, there is discomfort in the stomach, liver or pancreas.
- The appearance of stiff pain in the ribs, indicating intercostal neuralgia.
- There are signs of thoracic chondrosis and compression - a similar pathology.
- There are problems with the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Feels nausea, heaviness in the stomach.
- In men, several libido may decrease. Problems occur in the genitourinary tract.
- When you stand or sit for a long time, severe discomfort occurs.
- There is a severe headache accompanied by dizziness. A migraine with an aura may occur.
- The patient often develops intercostal neuralgia.
- The pain may radiate to the neck or lower back.
If you find in the totality of thoracic osteochondrosis and its signs or some of them, it is urgent to consult a therapist, neurologist, orthopedist. Also, such symptoms should be warned in the absence of problems with the gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular system and lungs.
There are both acute and subacute symptoms. If in exacerbation of osteochondrosis of the chest the patient experiences severe pain that deprives the patient of ability to work and he can observe only bed rest, then the subacute course is slow and does not significantly limit the patient's motor activity.
A clear sign of a sluggish lesion - no sharp pain. The symptoms in the subacute stage are erased. There is no discomfort with basic body movements, including inhaling, sneezing or turning. One does not suffer from pain in sleep, so the process of falling asleep is facilitated.
In order not to worsen the subacute course of the disease and to enter remission, important rules must be observed:
- Lifting weights is prohibited.
- You can't bend sharply.
- It is forbidden to sit or stand for a long time. One often unknowingly in this condition takes a position that is harmful to the spine, so there is an excessive load on the ridge, which leads to a new exacerbation.
- Avoid hypothermia. It has been proven that non-compliance with a comfortable temperature regime for the body turns into an exacerbation of the inflammatory process. Humidity is also harmful to the joints.
The duration of the subacute course is individual. If you follow medical recommendations, the patient will completely get rid of the discomfort within 2-3 weeks. If conservative treatment and rest do not help and the patient begins to suffer from nausea, dizziness and weakness, you should urgently consult a specialist. Such symptoms indicate re-exacerbation.
Degrees of development of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region
There are 4 clinical stages of the disease, at the onset of which the patient develops signs of pathology:
- There are no clinical symptoms in the initial stage. The first stage occurs against the background of the appearance of destructive processes in cartilage and bone tissue. In the first stage, there is also no rupture or stretching of the fibrous ring, so there is no hernia. They may detect initial bulge and signs of cartilage degeneration.
- The second stage is manifested by slight pain or discomfort. The attentive patient seeks medical attention, which is why osteochondrosis of the chest area is detected immediately. People who do not want to visit a specialist can still endure the second stage using available funds, but self-medication will not be enough for a long time. At this stage, the most common neurological symptoms may occur, including headache, burning in the interscapular area, neck pain and blood pressure spikes. Also at this stage there is an increase in degenerative destruction of the spine: the fibrous ring protrudes, which leads to the appearance of an intervertebral hernia of the thoracic region.
- The third stage is already difficult for the patient. Persistent neurological syndromes develop, including persistent radiating pain in the shoulder blades, arms, clavicle, and lower back. The patient may show somatic and autonomic disorders, indicating a disturbance in the functioning of the nervous system. The patient is often tormented by nausea, constant headache, dizziness, back pain. Concealed cardiac, gastroenterological or pulmonary signs of the disease may also occur. At this stage there is an active demineralization of bone and cartilage tissue. There is a tendency to injury.
- The last stage is the fourth. Against the background of osteochondrosis and hernia, irreversible consequences occur - the mobility of the intervertebral discs is completely lost, and the cartilage tissue at the site of a long course of inflammation is replaced by osteophytes. Surgery is needed to remove them.
In order not to bring the body into a condition similar to stage 3 or 4, it is better to see a doctor at the slightest sign. The sooner the disease is detected and therapy is started, the sooner the patient will return to normal and learn to live with osteochondrosis. The pathological destructive process cannot be completely stopped, but it can be slowed down by leading a healthy lifestyle, using medication and daily gymnastics. The later the patient sees a doctor, the more difficult it is to stop the severe pain syndrome associated with cartilage degeneration.
Risk factors and causes of the disease
There is no exact cause that causes destructive changes in the spine. An important role in the occurrence of pathology is attributed to a hereditary factor. It has been shown that people suffering from physical inactivity are more likely to have ridge problems than those who exercise regularly. Excessive physical activity can also provoke the destruction of cartilage at an early age.
Thinning and destruction of the intervertebral discs is closely related to the overload of the spine. If the muscles are not strong enough and the back is subjected to regular overload, there is destruction of cartilage tissue.
What causes osteochondrosis:
- Obesity. When you are overweight, there is strong pressure on the spine. As a result, premature destruction of bone tissue occurs.
- The presence of an anomaly in the structure of bones and cartilage. Such problems arise even during the period of intrauterine development.
- Congenital asymmetry of the intra-articular gaps in the intervertebral joints of the type of tropism anomaly, contributing to the appearance of a degenerative-dystrophic process in the spine.
- The presence of muscle spasm, spondylosis, chronic persistent trigger points and vascular disorders in the chest area. These pathologies also contribute to the appearance of osteochondrosis of the chest area.
- Prolonged vibration exposure of the spine in a sitting position. An example of a job is a minibus or bus driver.
- Frequent physical activity associated with heavy lifting. Examples of this are working as a loader or professional sports activities.
- Smoking and alcohol abuse. People with unhealthy lifestyles are more likely to have a lack of minerals in their body and poor circulation, which leads to back problems.
- Sedentary way of life. Insufficient physical activity causes accelerated calcium recovery, which is associated with poor metabolic processes. As a result, the bones become brittle. Also, muscle tissue atrophies, due to which the load on the spine increases significantly. The result is pain, frequent discomfort with minimal exercise.
Due to the intervertebral discs, sufficient mobility of the ridge is ensured. Intervertebral discs play a cushioning role. With the development of osteochondrosis, an accelerated process of demineralization occurs, the vital moisture from the joints is lost. This leads to discomfort, reduced mobility in the spine.
Risk factors for osteochondrosis of the breast include:
- Old age. In older people, natural degeneration occurs, which is why after 40 years the disease is found more often.
- Female. In girls, there are periods that contribute to the active extraction of calcium from the bones - pregnancy and menopause. Without adequate pharmacological support, spinal diseases tend to occur.
- The presence of hormonal disorders, endocrine diseases. If the patient has diabetes mellitus or uncompensated hypothyroidism, degeneration of the intervertebral discs may occur at an early age.
- Prolonged immobilization. If the patient is ill and has to lie down for a long time, atrophic processes occur in the muscles, which causes back pain.
- Previous back injuries. When the tendons and ligaments are stretched, the risk of osteochondrosis in the chest area increases.
- The presence of scoliosis. Poor posture in the future provokes serious problems with the spine, including osteochondrosis and hernias.
Diagnosis of thoracic osteochondrosis
If the patient suspects back problems, it is necessary to consult a therapist. The doctor conducts a general examination of the patient, asks for complaints, measures blood pressure. If there is a suspicion of a neurological problem, the patient is referred to a narrow specialist - traumatologist, neurologist or orthopedist.
At the meeting with a specialist, they also ask about complaints, conduct an initial diagnosis of the patient. Based on a visual examination, a set of diagnostic measures is prescribed, including:
- Radiography. With the help of an X-ray you can assess the condition of the skeletal system as a whole. If the patient has a hernia or osteochondrosis, hints of pathology may be observed - the distance between the intervertebral discs will be reduced and sometimes a darkening of the site of the suspected hernia is observed. If the image results do not match the specialist, you should continue to look for the cause of the pain and discomfort.
- CT or MRI. The most accurate diagnostic methods that allow you to accurately examine the condition of the source of inflammation in the picture. A more detailed image can be seen on MRI, but if there are contraindications (presence of a pacemaker or prostheses in the joints), computed tomography is prescribed. CT is an enhanced X-ray that allows you to see in detail the bones, tendons and ligaments. The image makes the image in the form of a three-dimensional image so that the details of the damage are clearly visible.
- Biochemical and general blood test. These tests are needed to assess the patient's health. If an increase in leukocytes, ESR, is detected, it indicates an active inflammatory process in the body. With active destruction of bone tissue in the blood are found reduced levels of calcium and deficiency of cholecalciferol (vitamin D3).
- Scintigraphy of the spine. The research method reveals active destruction of bone tissue. Weak bone tissue is highly susceptible to fragility. The method will reveal the tendency and signs of degeneration.
To diagnose the disease, you need to see an experienced specialist. A complete clinical picture is required for the final diagnosis, taking into account several laboratory test methods.
Thoracic osteochondrosis of the spine requires differentiation along with the following pathologies:
- Dyshormonal spondylopathy.
- Pathologies of the urinary system, including urolithiasis, cystitis or pyelonephritis.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system, with the exception of sinus arrhythmia, tachycardia and angina pectoris.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, including chronic pancreatitis, gastric and duodenal ulcers, irritable bowel syndrome.
- Previous injuries, fractures.
- Tumors in the chest, including malignancy.
- Rheumatoid arthritis (determined by a blood test for C-reactive protein, a rheumatic test and an ESR).
- Osteomyelitis of the spine.
- Acute inflammatory process.
- Ankylosing spondylitis.
- Spondylolisthesis.
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
An integrated approach to therapy is needed to slow the progression of the disease. In the initial stages, only conservative therapy is indicated, consisting of the use of drugs and physiotherapeutic methods of treatment. In advanced cases, when the patient has large hernias and a pronounced degree of bone degeneration, surgery is prescribed. Do not self-medicate at home. Folk remedies do not eliminate osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine.
In which cases is an operation performed?
The started osteochondrosis of the chest area negatively affects the quality of life of the patient. If the patient has constant discomfort that interferes with normal life, given the lack of effect of drug treatment, then a surgical solution to the problem may be offered.
Absolute indications for surgery include:
- Lack of sensitivity in the bladder and intestines.
- If the sensitivity in the legs disappears and the patient loses the ability to move independently.
- Paralysis due to strong growth of the hernia.
In other cases, the patient decides to remove the hernia formation on his own. If the disease really brings great pain and the patient's condition does not improve against the background of conservative treatment, doctors recommend surgery.
Drug treatment of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
During the period of exacerbation, the doctor prescribes various drugs needed for use to relieve the inflammatory process. The acute period is characterized by severe pain that can only be relieved with medication. If enough medication is taken, the patient recovers. Only an experienced specialist can prescribe medication; self-medication is unacceptable.
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is treated with the following drugs:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, painkillers or analgesics. These drugs are designed to quickly relieve back pain associated with an active inflammatory process. The effect of taking pills or injections is felt the next day. Taking any NSAIDs is accompanied by long-term side effects, which is why experts recommend limiting the use of the medication to a minimum period of no more than 1-2 weeks. Painkillers are most harmful to the stomach lining, causing gastropathy and inflammation. Patients at risk receive certain medications designed to protect the gastrointestinal mucosa. Examples are proton pump inhibitors, H2 histamine receptor blockers, antacids. People with ulcers and gastritis are better to avoid the use of NSAIDs or to take modern analogues with a selective effect.
- Muscle relaxants. These drugs are very effective in treating muscle spasticity. Relieve the pain associated with muscle tension. They act on the trigger points located in the pinched muscle tissue. The more a person gets tired, the greater their number. Muscle relaxants remove muscle contraction well and therefore have an analgesic effect. You must take medication in a course, the average duration of therapy is at least 2-4 weeks.
- B vitamins. Assignment of B1, B6, B12 in the form of injections with a combined composition. In large doses, these substances have an analgesic effect and have a positive effect on the nervous system. Neurotrophic drugs are effective in treating pain associated with pinched nerve roots. With the help of nutrition it is impossible to meet the norm of these substances needed to achieve a therapeutic effect, which is why they are prescribed in the form of drugs. The average duration of a course of injections is 2-3 weeks. Then, if necessary, switch to tablets.
- Anti-inflammatory ointments, gels. If the pain is tolerable and systemic forms of NSAIDs are contraindicated, external drugs are prescribed. The advantage of external means is that they do not cause side effects. In rare cases, skin allergies may occur, but the ointment will not cause deterioration of the gastrointestinal or laboratory blood. Another advantage of outdoor products is the possibility of long-term use. You can rub the gels for up to 4 weeks, after which they take a break. The scheme and duration of therapy are determined by the attending physician.
- Honoprotectors. These are complex substances used to nourish the cartilage of the joints. It is necessary to use drugs for a long course, at least six months, after which a break of 2-3 months is made and the course of therapy is repeated. Injectable forms of release are used within 2-3 months, as they are better absorbed. They then switch to maintenance treatment, including the use of tablets. It is important to understand that drugs do not stop the destruction of cartilage tissue. They only create additional nutrition, which slows down the degenerative processes taking place in the bones and joints.
- Complex preparations of calcium and vitamin D3. It has been proven that people in the northern latitudes do not get enough vitamin D3, as solar activity is low all year round in this region. To get rid of hypovitaminosis, it is necessary to take cholecalciferol supplements in winter and autumn in courses, while solar activity is minimal. Without this vitamin, the assimilation of calcium and other minerals is impossible. Due to a long calcium deficiency, over time there is a thinning of bone tissue, so a person suffers from osteochondrosis and other complications. Calcium and D3 are better absorbed in combination, which is why complex preparations are prescribed. The dose and course of administration should be prescribed by your doctor.
In addition to treatment, homeopathy, antispasmodics and complex multivitamins may be prescribed.
Conservative therapy for osteochondrosis of the breast
During the recovery period, the patient should pay sufficient attention to rehabilitation. The more carefully the patient maintains his health, the rarer the attacks of the disease will be.
The most effective conservative treatments include:
- Exercise therapy. With the help of exercises the patient learns to keep his back straight, strengthens the muscular corset. Physiotherapy can be done at any age, several times a week. The complex is selected individually, taking into account the anatomical features of the patient. Start the performance gradually, at the beginning taking no more than 5 minutes a day. With the improvement of physical qualities, the patient learns to do more difficult exercises for a longer period of time.
- Supporting corset. Anatomical devices are used to support weakened muscles, if there are contraindications for their strengthening. The patient chooses a bandage depending on the height and type of appointment. The attending physician should select the appropriate model. The duration and model of wearing are determined individually. You cannot wear a corset around the clock, otherwise the muscles of your back will become even weaker.
- Massage. In medical practice, massage is one of the most popular and at the same time effective methods of conservative treatment in the presence of osteochondrosis of the chest in a patient. During the recovery period, the muscles need extra support. It is useful when the blood flow is temporarily improved and the overstretched muscles are relaxed with the right technique. You should attend specialized sessions several times a year in courses.
- Physiotherapy. Physiotherapy procedures are widespread in traumatology, orthopedic and neurological practice. With the help of procedures the local blood flow is improved, systemic drugs are used externally and the device acts on the damaged tissues. As a result, the muscles heat up and the chronic inflammatory process is eliminated in the affected area. Examples of medical procedures - magnetic therapy, shock wave therapy, electrophoresis.
Manual therapy and acupuncture are less commonly prescribed.
Osteochondrosis of the chest region is a serious disease if it has started. To prevent the course of the disease acutely, a comprehensive treatment of the pathology is needed.

























